Constructing Expressions
You construct expressions in the Expression EditorEditor in which to create expressions..
About Expression Syntax
You must enclose a function, field reference, or calculated expression in an expression bracket. This syntax is a dollar sign with parenthesis, as follows:
$( )
The $( can only appear as the outer most portion of the expression, and should not appear anywhere within the expression itself. If you enter $( anywhere else within the expression, the current parser cannot interpret the expression properly, and incorrectly interprets the entire expression, as if it were a regular string literal.
In certain cases, the parser does allow for expressing simple values, without requiring the use of $(). An example is expressing simple string literal values such as "active".
About the Expression Editor
When you create or edit an initialization rule, editing rule, calculation rule, read-only rule, required rule, or before-save rule, you use the expression editor.
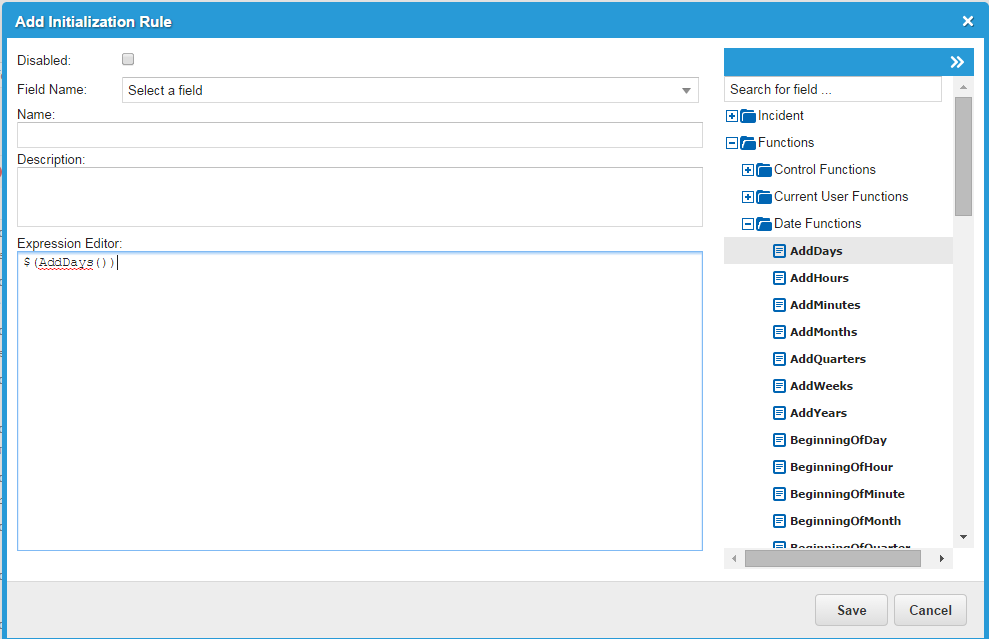
Using the Expression Editor
You can customize business rules by using expressions.
| 1. | In the Configuration Console, go to Build > Business Objects > Incident > Business Rules. |
| 2. | To add a new business rule, click Add <type of rule> Rule. For example, to add an initialization rule, click Add Initialization Rule. The Add Business Rule window appears. |
To edit an existing business rule, click Edit  . The Edit Business Rule window appears.
. The Edit Business Rule window appears.
| 3. | In the Expression Editor, enter an expression or drag a function from the Functions drop-down list to the Expression Editor. |
| 4. | Click Save. |
About the Expression Validator
HEAT Release 2014.3 adds an expression validator. The expression validator provides informational messages about expression syntax.
At this time, the expression validator is only used for business rule and form expressions and not for relationship expressions or other types of expressions.
When you create or edit a business rule, you use the HEAT Expression Editor. If you enter something incorrectly, for example if you misspell an expression name, the expression validator returns a warning or error message and provides a hint about the problem.
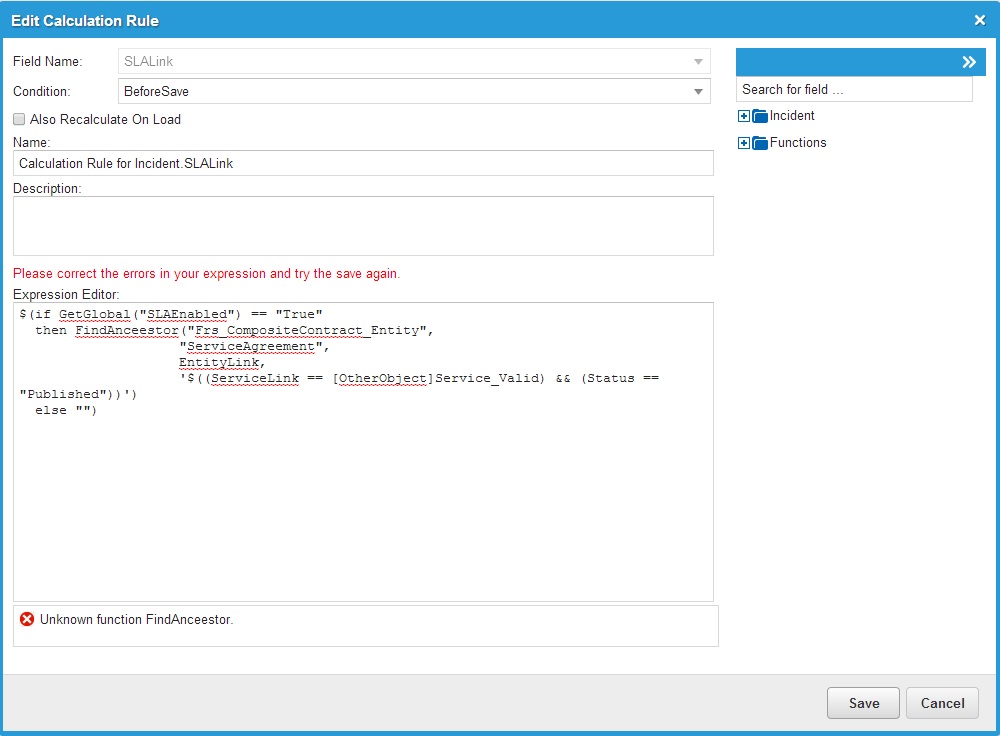
In the following example, the name of the built-in function FindAncestor is misspelled. The expression validator provides an informational error message and does not allow you to save the expression.
Expression Editor Validation Message Example 1
In this example, the syntax is wrong and the validator displays an error message:
Expression Editor Validation Message Example 2
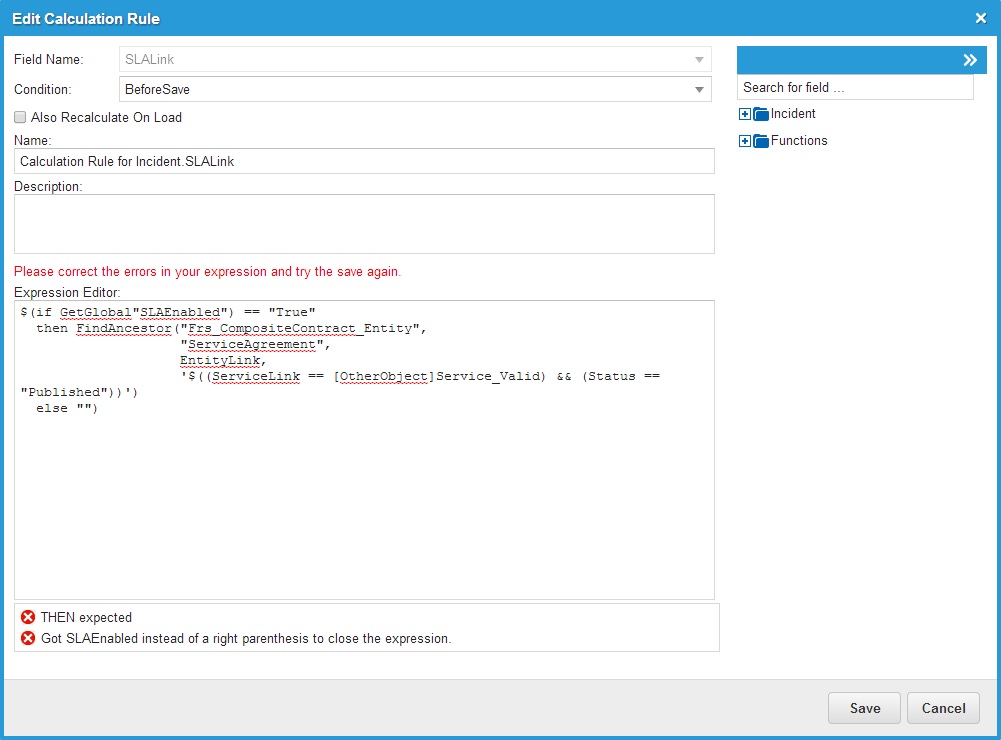
The expression validator checks all parts of the syntax, including the names of constants to ensure that they are valid. If it finds an invalid constant, the expression validator returns a warning message and allows you to save the expression.

|
In future releases of HEAT, the expression validator will return error messages and will not allow you to save the expression. In HEAT Release 2014.3, the expression validator only returns warning messages and allows you to continue, even if there is an error. |