ITILInformation Technology Infrastructure Library. A set of practices for HEAT that focuses on aligning IT services with the needs of business. defines Problem ManagementA process designed to eliminate recurring incidents from the IT infrastructure. as a process designed to eliminate recurring incidents from the IT infrastructure. A problem is identified by multiple incidents exhibiting common symptoms or a single incident with no known cause.
An incidentA event indicating an interruption or reduction in service. is an unplanned interruption or potential interruption to service. A problemMultiple incidents exhibiting common symptoms or a single incident with no known cause. is the underlying root-cause of one or more incidents or potential incidents. Problems and incidents are distinct, and represent separate situations and activities. An incident becomes a problem when an incident has no workaround, or if there are recurring incidents affecting the same services or configuration items. A problem is identified after resolving one or more similar incidents.
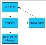
Incidents where the root cause is unknown are identified as problems. When the root cause of such problems are identified, it might result in the resolution of the related incident and the problem becomes a known error. To implement a workaround or fix, problems might result in requests for change. The following diagram shows the relationship between the three IT processes:
Incident, Problem, Change Relationship
Problem Management manages the lifecycle of all problems. The primary objectives of Problem Management are to prevent incidents from happening, and to minimize the impact of incidents that cannot be prevented. Proactive Problem Management analyzes incident records, and uses data collected by other HEAT processes to identify trends or significant problems before they are logged as problems.
Incident Management and Problem Management are closely linked. Problem Management attempts to identify and resolve potential problems before they become incidents.

|
While Incident Management and Problem Management might seem similar, they have different goals. Incident Management resolves an issue and restores services quickly; often by applying a workaround. Problem Management identifies the root causes of incidents, determines a permanent resolution, and formulates a prevention plan. |
The HEAT application models the Problem Management sub process activities as defined by ITIL.
This sub process consists of the initial logging of the problem. Logging the problem introduces the problem record into the system.The initial recording of a problem, including all relevant information that is available when the problem occurs, is part of this sub process.
Problems can be logged from incidents, or they might occur when implementing a change or release. The problem logging sub process also includes notifying the appropriate person or group that there is a problem and a need for assistance.
Problems can also be logged by the Problem Manager proactively monitoring incident trends or failures. For example, monitoring the default incident dashboards called All Incidents by Service or Active Incidents by Service this Year help the Problem Manager determine whether some of the service failure incidents are in fact due to a problem in the infrastructure.
When a problem is logged from another source, the Problem ManagerResponsible for managing the lifecycle of all problems. The primary objectives of the role are to prevent incidents from happening and to minimize the impact of unavoidable incidents. The Problem Manager undertakes research for the root causes of incidents, and tries to make sure that interruptions are eliminated. or Problem Review BoardA group of people who manage problems. This is done through analyzing incidents as they happen, reviewing historic trend data, and staying current with industry news and vendor updates. The PRB must include representation from relevant individuals to effectively review incident trend data for reactive Problem Management as well as searching for risks from a proactive stance. determines whether the logged problem is in fact a problem. During the Investigation sub process, the Problem Manager might assign the problem to an owner and team, select members from the Problem Review Board to review the problem, search the knowledge base for solutions, create tasks for the problem, and so on.
Examples of a problem might be an outage, an incorrect or an unusual result. Problem investigation encompasses the collection, analysis, and correlation of data to determine and isolate the cause of the problem.
After the identification sub process, the problem is in active state. Problems might need to be correctly classified by their category and then prioritized by impact and urgency. See Default Priority Values.
Identification of configuration items or services as the root cause of the problem might be identified. The problem dashboard part called Active Problems with Linked CIs, for example, might help in this identification. During the problem identification period, tasks are created and assigned as steps to resolve the problem. A fix to the problem might require a resource or a vendor to work on the problem.
During the resolution sub process, the identification, implementation, and verification of the solution is carried through. A temporary resolution or workaround might be created and made available to solve current and future incidents arising from the problem. Notification is sent to the affected users and owners.
Proactive notifications to requesters and other stakeholders, escalations, and reporting can be done throughout the problem life cycle to make sure that the goals of successful problem resolution are being met.
Problem Managers can also view the cost of the problem while it is worked on, and get a final cost associated with the problem upon the problem's resolution or closure.
After problems are closed, they remain in the database and are viewable for reporting and analytical purposes. Problem Managers can view and generate dashboards and reports to view problem metrics and scorecard data.
| 1. | Log into the Configuration Console and click the Home tab. |
| 2. | View the defined dashboards. |

|
You might not see all the dashboards that are available to your role. To select and display all the dashboards that are available to your role, see Using Dashboards. |
| 3. | Click any of the data labels on the charts to see more information. Double-click any of data labels on the charts to activate a search on the label, the results of which are displayed as a list on the Problem tab. |
For example, if you are viewing problem by category (which categorizes problems and drills down to the problem category by status) and you click any of the data labels, a list of problems that have a similar status by category is displayed in the search results list on the Problem tab.
| 4. | Double-click any of the rows to open the problem record. |
Open the Problem workspace. A list of all the problems, arranged from the highest problem ID appears.

|
The application of the data-segregation security organizational unit constraint to a role can affect the list of records that appear by default. If you do not see the default list of records in the search results grid, you might need to select a different search from the saved searches menu. |